# Sounds like English
# About /ə/
/ə/ is called "schwa" (中元音), Schwa is the most common vowel in English. /ə/ is always unstressed.
How to pronounce?
- Jaw: relaxed
- Lips: relaxed, 微张,气流平出,
- Tongue: at the bottom, relaxed
因为发音较短,还没有到达 /ɛ/ 或者 /æ/ 的位置。
system action about problem today
除了音标本身的 /ə/ 外,还有一些句子中不影响句子含义的小词也会有 schwa 现象。
The words that are often unstressed and have an /ə/ in them are prepositions (e.g. to, of), pronouns (e.g. them, your),and articles (i.e. a, an, and the).
E.g. We've run into an issue.
# About /æ/
嘴型更宽,stressed,
- Jaw: dropped (lower than when pronouncing /e/) lowered a lot
- Lips: stretched sideways,张嘴,气流向下,tense
- Tongue: tense; kept down low, pushed forward
man * tap * chat * sat * pan * bad * can't * app * map * pad
Examples of the Vowel [æ] (opens new window)
如果 /æ/ 遇到了 /ŋ/,/æ/ 的发音就 more like /ei/ gang
# About /ɛ/
这是一个 stressed 音,比 /ə/ 发音要长,舌头抵住下齿,
Jaw: slightly lowered Lips: relaxed Tongue: pushed to the front, relaxed, raised in the middle
red never embrace enter embody desk
# About /eɪ/
/eɪ/ is diphthong. Make the /ɛ/ sound first, then...
Jaw: lifts up
Tongue: lifts up to the roof of the mouth
Lips: widens
late * take * main * fail * blame * lady * break * maintain * Spain * frame * brain * great
这个音由 e i 组合发音,i 这个音不能省略,Yoga 这个 i。
# About /ʌ/
- Jaw: dropped
- Lips: relaxed, unrounded
- Tongue: tip of the tongue - forward, back - slightly down
luck * lunch * cup * but * bug* cut * stuff * fun* month * does
# About /ɑː/
Jaw: very low
Lips: relaxed, resting
Tongue: very low, flat
lock * cop * hot * bot * sock * block * box * dot * job * got
这些词在美音中发 /ɑː/,在英音中更多的读作类似 /ɔ/
# About /aɪ/
Make the /ʌ/ sound first, then...
Jaw: lifts up
Tongue: lifts up to the roof of the mouth
Lips: widens
- time * find * byte * reply * skype * deny * provide * strive * tonight * finalize * supervise * decide * guide *
# About /aʊ/
Make the /ʌ/ sound first, then...
Jaw: lifts up
Tongue: the back of the tongue raised
Lips: round
brown * bound * now * found * cloud * sound * down * account * announce * power *

# About /ɔ/
Jaw: dropped
Lips: round, flare
Tongue: pulled back
- on * off * cause * saw * blog * boss * bought * call * caught *dot
pure unstressed: on runoff lifelong
pure stressed: saw boss long login wrong daughter
/ɔ/ modified by /r/: core
# About /ɔɪ/
Start with the /ɔ/ and then:
Jaw: lifts a little
Lips: widen
Tongue: a bit lifted
enjoy * avoid * appointment * choice * deploy * employ * join * loyal * noise * point
stressed: boy coin joyful
unstressed: loyal
# About /oʊ/
Start with the /ɔ/ and then:
Jaw: lifts a little
Lips: round
Tongue: the back part stretches up
go * phone * so * home * note * bold * chose * show* close *cold
/ɔ/ or /oʊ / or /ɔɪ/ (opens new window)
# About /l/ and /ł/
English L that is close to the beginning of the syllable is called light /l/. It usually goes before a vowel or diphthong in a syllable.
English L that is close to the end of the syllable is called dark /ł/. It goes after a vowel or a diphthong. 这个发音重要的是在发音结束后,舌头抵住上牙龈。
low * level * lack * layer * launch * lunch * feel * call * tool * deal * email * fail
# About /ɹ/
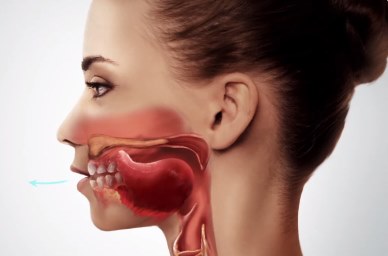
Tongue: the top of the tongue is lifted, is kind of "rolled".
# About /m/
Jaw: dropped a bit
Lips: pressed together
Tongue: relaxed
The air comes through the nasal passages.
makemarkmovemeetblameframehomeshamescrum*claim
# About /n/
Jaw: slightly dropped
Lips: relaxed
Tongue: wide, lifted to the roof of the mouth
The air comes up through the nasal passages.
nevernetnoiseninefinephonemaingainwinwhentone
# About /ŋ/
Jaw: slightly open
Lips: relaxed
Tongue: the back of the tongue is wide and raised, touching the soft palate
The air comes through nasal passages.
pingsingleEnglishalongshoppingsingringthingbring*calling
/n/ or /ŋ/ 最主要的区别在于 /n/ 是 non-nasal /ŋ/ 是 nasal 音。
# About /w/
Jaw: slightly open
Lips: tight, round
Tongue: lifted in the end
Vocal cords: closed
Release the air and spread your lips. 口型呈O型。
weather * walk * when * weekend * work * Wednesday * web * wait * wide * well *
# About /f/ and /v/
/f/:
- Jaw: fairly closed
- Lips: bottom lip vibrating against the upper teeth
- Tongue: relaxed to let the air push through
- Vocal cords: off
How to make the /v/ sound:
- Jaw: fairly closed
- Lips: bottom lip vibrating against the upper teeth
- Tongue: relaxed to let the air push through
- Vocal cords: on
- the /f/ and /v/ sounds differ only in the work of the vocal cords
/v/发音技巧:bite the bottom lip
fine * feel * form * staff * half * vacation * value * voice * leave * dev * improve * event
# About /s/ /z/
- Jaw: almost closed
- Lips: relaxed
- Tongue: the tip - down, lightly touching the back of the bottom teeth
- Vocal cords: off /s/
- Vocal cords: on /z/
牙齿闭合,舌头往下,There is a little tension in the tongue.
sorry * so * say * submit * sample * scratch * script * send * story * same * scenario
lose * freeze * size * zoom * busy * news * raise * Thursday * reason * puzzle * observe *
# About /θ/ /ð/
- Jaw: almost closed
- Lips: relaxed
- Tongue: relaxed, the tip comes through the teeth
- Vocal cords: off/on
牙齿咬住舌头
think * third * Thursday * through * thought * thousand * theory * thin * path * truth
then * there * other * they * this * those * though * thus * another * either * further
# About Connected Speech
# 1. Elision
It means omitting one or more sounds in a word or phrase to make it easier to pronounce.
eg. The handsome movie star acts in a film about friendship between a father and son.
When T or D comes between 2 consonants at the end of a syllable (or even between 2 words), the T/D doesn't get pronounced.
Practice: * friendship * facts * tactful * dialects * attempts * postcard * postman * postdate * handsome * most popular * father and son
# the elision of /h/
- Did he get it?
- Diddy get it?
- DI-diy Gɛ-dit
is he * might have * should have * could have * must have * see him * see her * saw him * saw her * around here
# the elision of /t/
- I want to go = "I wanna go"
- I am going to go = "I'm gonna go"
Elision (because it happens when a sound disappears or is "eaten" by other stronger or similar sounds next to it)
Wanna come here * gonna show him * wanna tell her * wanna work from home * gonna work from home * gotta go * gotta like her * gotta ask him * wanna wait here * gonna have it *
# 2. Assimilation
Assimilation is when two sounds meet and then they form a third sound. You often get this between words.
| Rule | Example |
|---|---|
| T + Y = "ch" | I want you to help. Nice to meet you. |
| D + Y = "dj" | Could you help me? Would you mind helping? |
want you * would you * could you * need you * meet you * did you * feed you * fed you * split you *
# 3. Linking
When a word ends in a consonant sound and the next word starts with a vowel, we move that consonant over to the beginning of the next word.
| Linking words | Phonetic symbol |
|---|---|
| An Apple | /ə næpəl/ |
| I love oranges | /aɪ lʌ vɑrɪndʒɪz/ |
- an Apple device * an orange mouse pad * at eight * at one * in America * in Australia * work at home * speak up * read on * step up * keep it *
# 4. Intrusive /r/ in connected speech
The intrusive /r/ pronunciation happens between two words, where the first word ends in a vowel sound (e.g. "where") and the second word begins in a vowel sound (e.g. "are").
Read the words and phrases below with the /r/ between the vowels.
saw a film * Brenda and Eddie * Lisa and Jane * China and Japan * media event * Canada and Vietnam * Russia and England * data of * data on * data about *
# About Word Stress
- Stressing means that speakers of English make certain syllables and words louder, longer and higher in pitch.
- De-stressing means that speakers of English make certain syllables and words more relaxed and weaker.
Sometimes word stress helps us tell similar words apart. For example, "project" is a noun which refers to implementation of a plan, while "project" is a verb, which could mean making future predictions.
| Word | Stressing1 | Meaning | Stressing2 | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| progress | /ˈprəʊ.ɡres/ | n.进步,进展 | /prəˈɡres/ | v.进步;改进;进展 |
| conflict | /ˈkɒn.flɪkt/ | n. 1.冲突;分歧;争论 2.战斗,战争 | /kənˈflɪkt/ | v.不一致;发生抵触;相矛盾;冲突 |
| contrast | /ˈkɒn.trɑːst/ | n. 差异;对照,对比 | /kənˈtrɑːst/ | v.差别,差异;对照,对比 |
| contract | /ˈkɒn.trækt/ | n.合同;契约 | /kənˈtrækt/ | v.1.(使)收缩;(使)缩小;(使)缩短 2.患上,感染(疾病) 3.(与…)订立合同;(与…)订契约 |
| import | /ˈɪm.pɔːt/ | n. 1. 进口商品 2. 进口;输入;引进 | /ɪmˈpɔːt/ | v. 1. 进口 2. 引入,引进 3. 导入;输入 |
| project | /ˈprɒdʒ.ekt/ | n. 1.项目;方案;工程 2. 课题,研究 | /prəˈdʒekt/ | v. 1. 预计,推算 2. 投掷;发射 |
| record | /ˈrek.ɔːd/ | n. 1. 记录;记载 2. 前科;病历 3. 履历;历史;经历 4. 唱片;单曲 5. 最佳纪录 | /rɪˈkɔːd/ | v. 1. 录制;录(音);录(像) 2. 记录;记载;记下…备案 |
| content | /ˈkɒn.tent/ | n. 1. 目录 2. 内容 3. 含量 | /kənˈtent/ | v. 使满意,使满足 |
| extract | /ˈek.strækt/ | n. 1. 提出物,精华,汁 2. 摘录;选段;引文 | /ɪkˈstrækt/ | v. 1. 取出;拔出;提取 2. 强索;设法获取 |
Pitch is the highness or lowness of your voice. We use pitch in order to express our emotions and attitude through a change in the tone of our voice. We also use pitch in order to express word stress. It's important to learn to change pitch because it affects /əˈfekt/ how well English speakers understand you.
# About intonation
Intonation is a term used to refer to the distinctive use of different patterns of pitch and frequency that carry meaningful information about the attitude of the speakers towards some information.
# Falling intonation
- We use falling intonation for statements.
I have to give stress to one of my content words. That's my focus word, and usually it's the final content word in a sentence.

Longer sentences break into ----> thought groups
Each thought group ----> has a focus word
So we say each thought group with one intonation pattern.
- We also use falling intonation in wh- questions.

# About rising intonation
- The rising intonation used with many questions, especially yes-no questions.

Rising intonation can express
- doubt
- uncertainty
- incompletion

